How Does Online Activation Work |
Online activation in HTML Executable requires a remote server with the necessary web application files installed. The ebook application software you built with HTML Executable directly checks and downloads user registration information from the server, allowing you to remotely control who can activate certificates and unlock registered editions of your ebooks.
Additionally, activation ensures that end users can only activate their key on a limited number of computers and that users who have received a refund can no longer access the ebook.
Activation Steps
1) The user places an order for your publication or ebook from your public application store or authorized reseller (for instance PayPal). The latter sends the user information to a dedicated application on your server. This application creates a client record with the user information and a license record in its database. It finally sends a unique activation key to the end user (by email for instance).
2) The user starts the publication and enters their activation key in the nag screen as shown below. They click Activate.
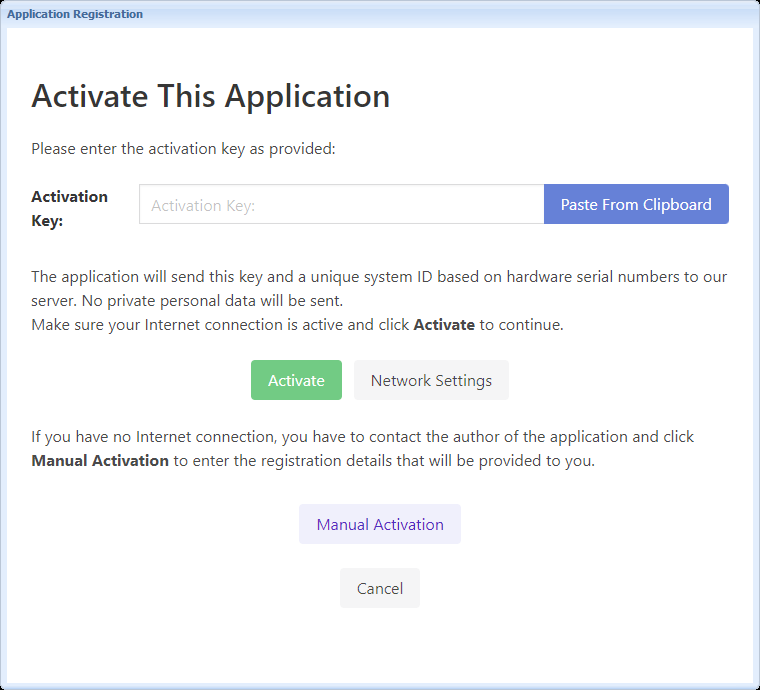
3) The ebook connects to the server application that manages activations, while passing parameters such as the activation key, the unique system ID. No private personal data is sent.
4) The application searches for the license record associated to the activation key in the database. If the account is found, it checks the number of allowed activations, whether the account is locked or not... The application then generates registration data (with the user's name, unique system ID...) and returns it to the publication or ebook.
5) The ebook then analyzes the registration data. If the activation is allowed by the server, the certificate is unlocked; otherwise, an error message is displayed.
✔ Everything is transparent and can be automated thanks to our online server application and/or controlled manually thanks to the online administration panel in your web browser:
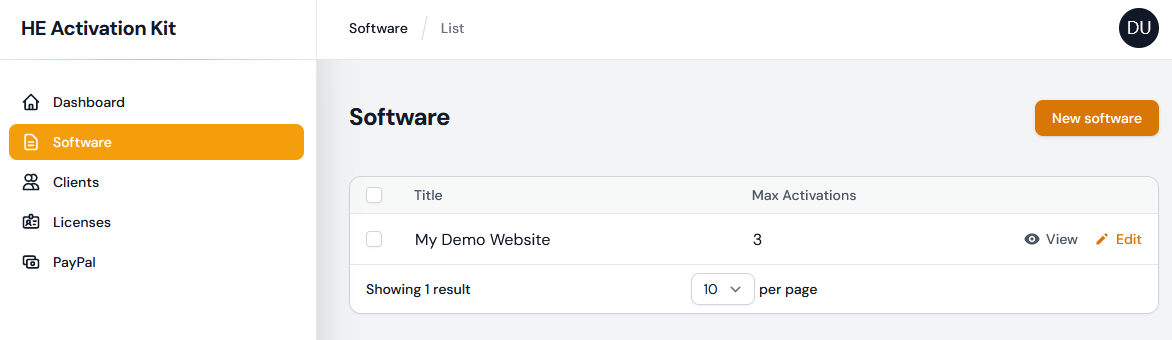
✔ Moreover, you can validate the access to the publication each time it is run for instance. This lets you control who can access your publication.